This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Introduction to AERMOD
AERMOD (American Meteorological Society/Environmental Protection Agency Regulatory Model) is an atmospheric dispersion model developed by the U.S. EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) in collaboration with the American Meteorological Society (AMS). It is designed to assess air quality by estimating pollutant concentrations emitted from industrial and other stationary sources.
This document is not only a tutorial for running AERMOD, but also a comprehensive technical guide. The objective is to simulate a real-world dispersion scenario in Bloomington, Illinois (IL), using:
- Wind minute-resolution data from AERMINUTE, covering the entire year of
2024; - Land cover data from the year
2023, as they are the most recent available for surface parameterization usingAERSURFACE; - Result visualization using the AERPLOT utility.
By completing this guide, you will not only learn how to set up and run the AERMOD modeling system, but also acquire all the technical skills necessary to apply it professionally anywhere in the world.
Purpose
AERMOD is used for:
- Assessing environmental impacts from atmospheric emissions;
- Checking compliance with air quality standards;
- Supporting environmental permitting processes;
- Simulating pollutant dispersion under different meteorological conditions.
How it works
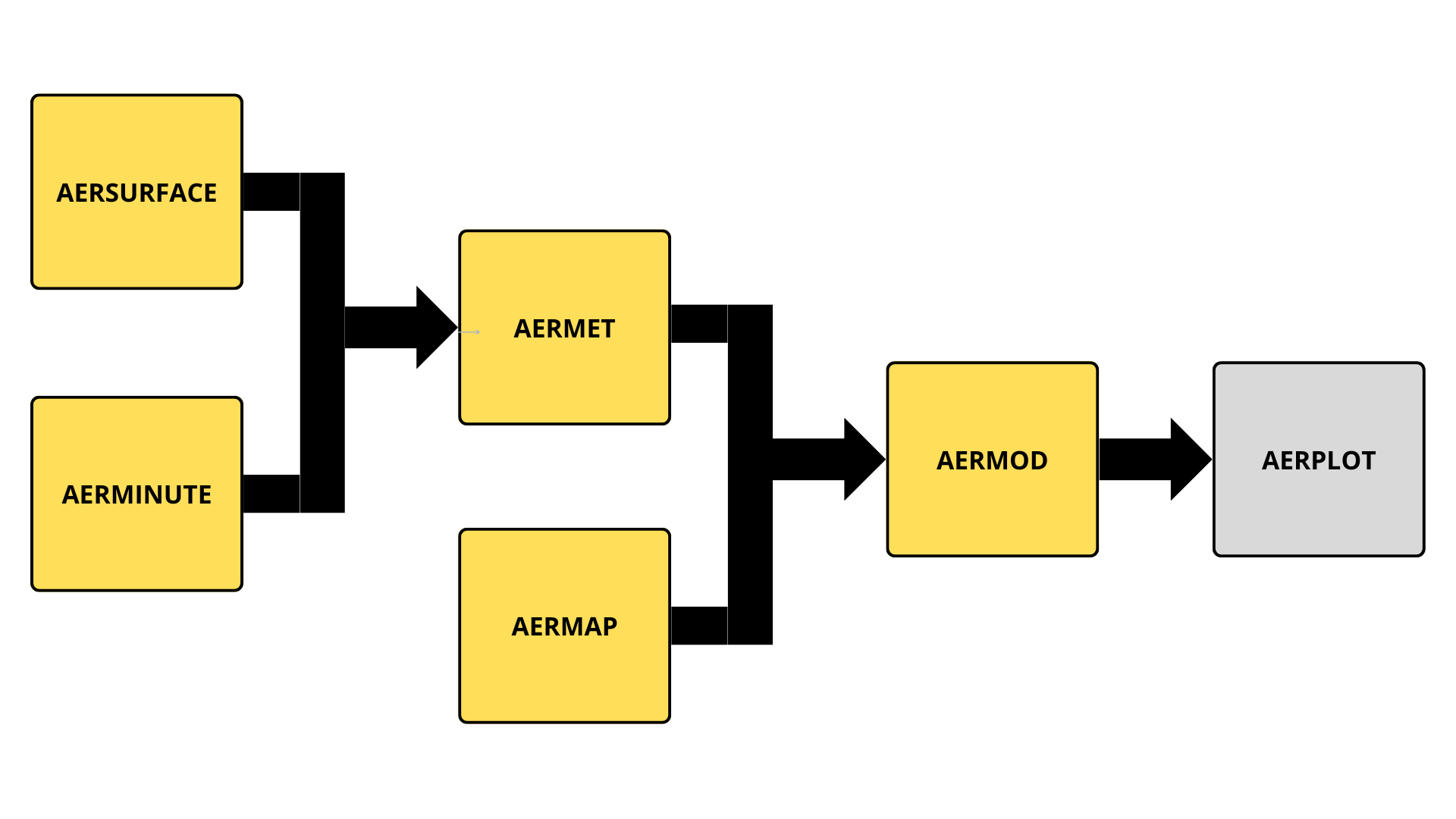
AERMOD simulates the transport and dispersion of pollutants in the atmosphere based on local meteorological conditions, terrain features, and emission source characteristics. The model requires preprocessed input data from auxiliary tools, including:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| AERSURFACE | Calculates land use parameters such as surface roughness, albedo, and Bowen ratio. |
| AERMINUTE | Refines hourly wind data based on 1-minute METAR/ASOS observations. |
| AERMET | Processes surface and upper air meteorological data (e.g., from radiosondes). |
| AERMAP | Determines terrain characteristics for each receptor location. |
| AERPLOT | Generates maps and visuals from AERMOD outputs to support interpretation and reporting. |
Na Figura 1 podemos observar o fluxograma desses processadores
…
Figura1
Using these inputs, AERMOD calculates hourly pollutant concentrations at specific receptor locations, accounting for:
- Horizontal and vertical dispersion;
- Atmospheric stability effects;
- Terrain elevation influences;
- Different source types (point, area, volume, and line sources).
Output
AERMOD output includes:
- Hourly, daily, monthly, or annual pollutant concentrations;
- Statistics for comparison with legal thresholds (e.g., percentiles);
- Pollution plume maps (when used with external visualization tools).
Typical Applications
- Chemical and petrochemical industries;
- Thermoelectric power plants;
- Landfills and incineration facilities;
- Environmental licensing studies;
- Emergency atmospheric release modeling.
Notes
AERMOD is recognized as a regulatory model by the U.S. EPA and is widely adopted internationally — including in Brazil — for environmental impact studies involving atmospheric emissions.