This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
2. AERSURFACE
2.1. Introduction
In this section, we will cover AERSURFACE, a preprocessor for AERMET that assists in characterizing land surface parameters. It defines three key values:
- Surface roughness length (Zo)
- Albedo
- Bowen ratio
| Task | Assist in obtaining values that characterize land use and land cover. |
|---|---|
| Input Data | Land cover, impervious surface percentage, and canopy percentage in GeoTIFF format. |
| Output Data | Surface roughness length (Zo), albedo, and Bowen ratio — to be used in AERMET. |
| Parameter | Definition | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Roughness (Zo) | A measure of terrain roughness — how much resistance the surface offers to wind flow due to obstacles like vegetation, buildings, and topography. | Defines the wind speed profile near the surface. Higher Zo generates more turbulence, which affects pollutant dispersion. |
| Albedo (Alb) | The proportion of solar radiation reflected by the surface. Ranges from 0 (fully absorbed) to 1 (fully reflected). | Affects soil heating and, consequently, convective turbulence (rising warm air bubbles). |
| Bowen Ratio (Bo) | The ratio between sensible heat (air heating) and latent heat (evaporation). It indicates whether heat is transferred more into the air or into evaporation. | Helps estimate surface heat flux, which is essential for calculating atmospheric stability (how well the air supports pollutant dispersion). |
2.2. Download the Executable
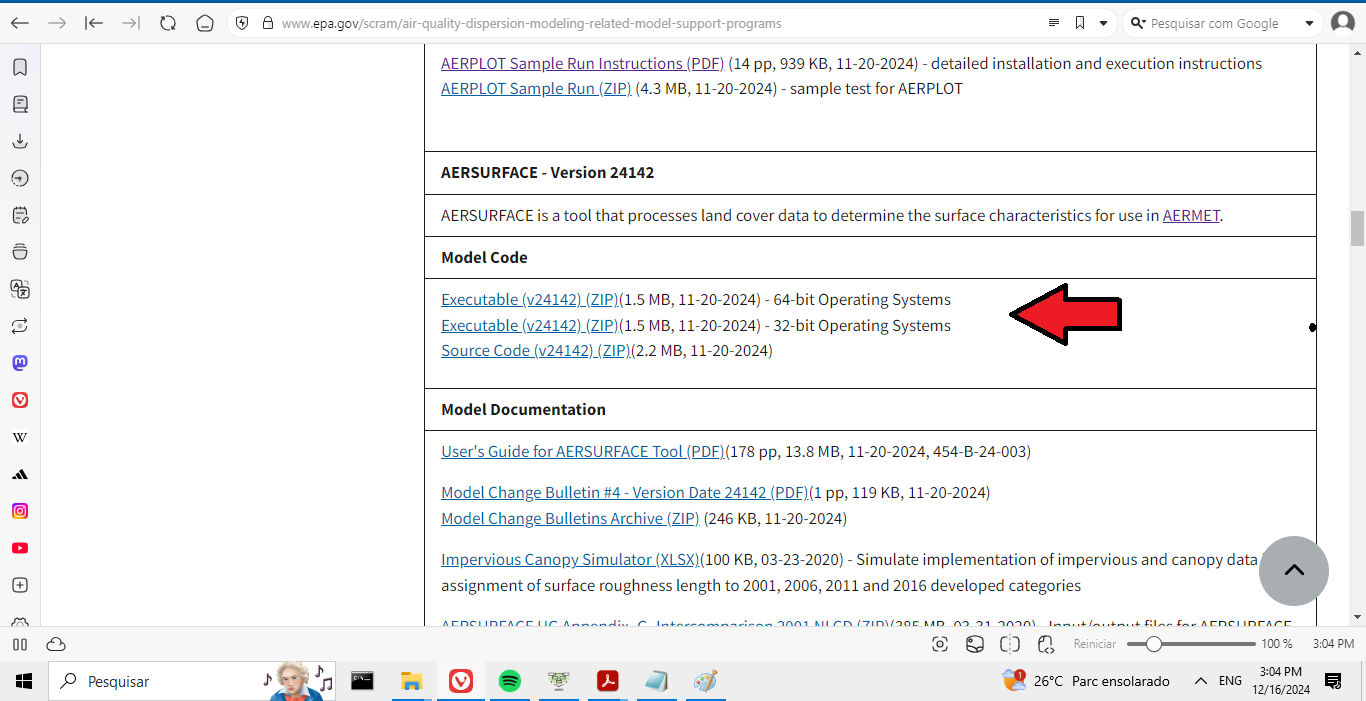
First, download the AERSURFACE executable:
Download the appropriate file for your operating system and save it to:
..\AermodTutorial\AERSURFACE\
In Figure 1 we can observe the download page.
Figure 1
2.3 Obtaining Surface Data
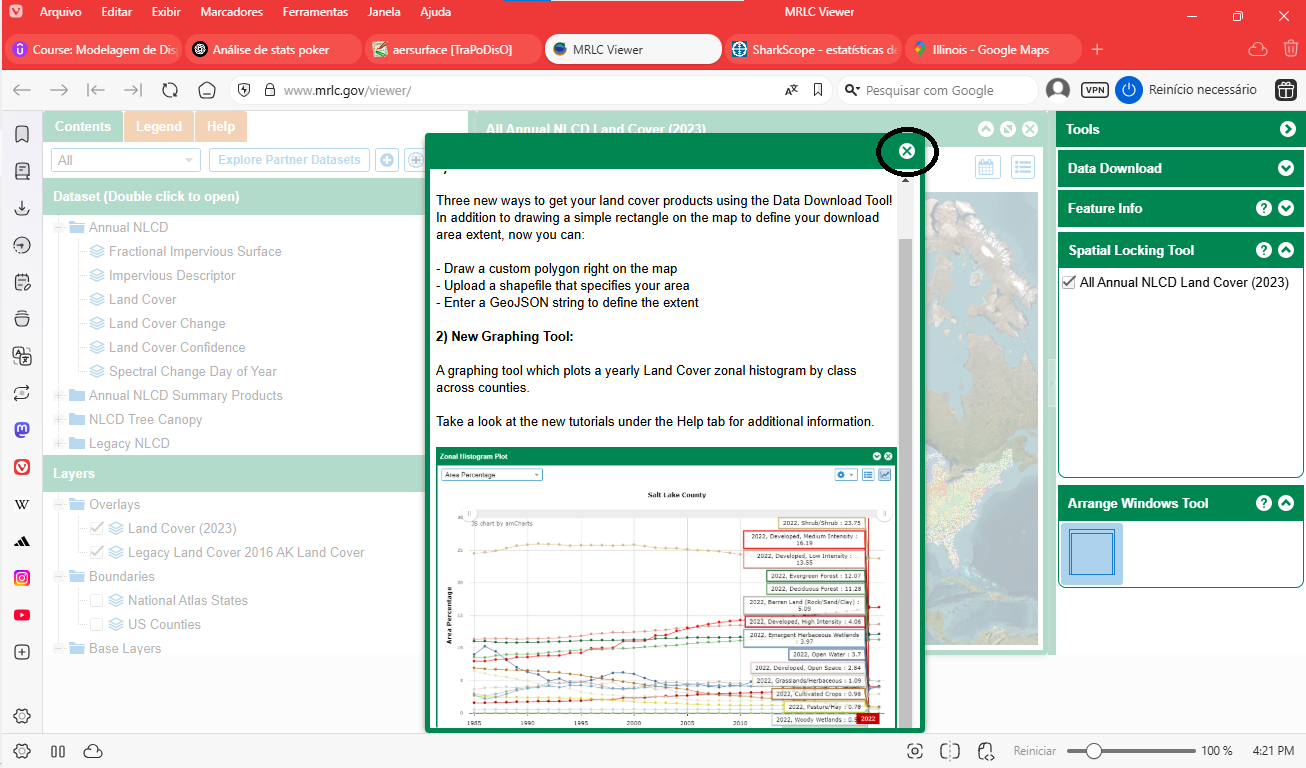
Go to: MRLC Viewer. Close the pop-up window as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
Enable only the National Atlas States and ESRI World Imagery layers. See Figure 3.
Figure 3
Use your mouse to pan and zoom to the USA, then locate the correct state. See Figure 4.
Figure 4
Next, locate the point `-88.9520 40.4471` using the mouse coordinates. See Figure 5.
Figure 5
Zoom in further as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6
Click the icon shown, and using the left mouse button, select your area of interest by clicking the two corner points. See Figure 7 and Figure 8.
Figure 7
Figure 8
Check the boxes exactly as shown, and set Select Years to 2023. See Figure 9.
Figure 9
Enter your email and click download. See Figure 10.
Figure 10
Check your inbox for a message from `no-reply@usgs.gov` and click the download link. See Figure 11.
Figure 11
Save the downloaded ZIP file to: `C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\1.AERSURFACE` Then extract its contents.
2.4 Preparing AERSURFACE Inputs
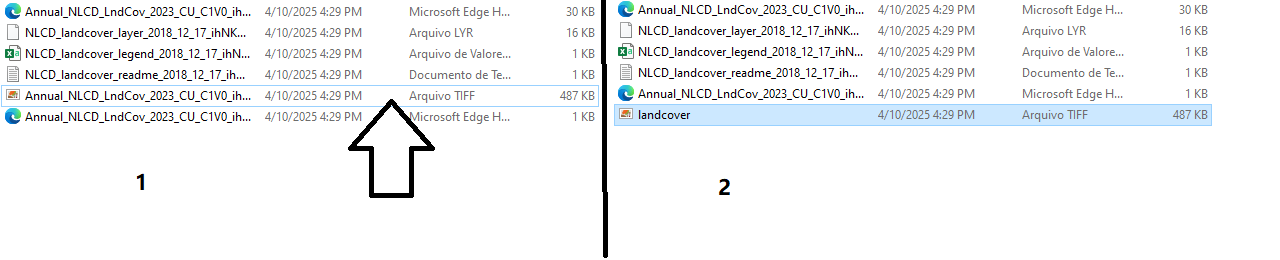
Rename the `.tiff` file to `landcover.tiff`. See Figure 12.
Figure 12
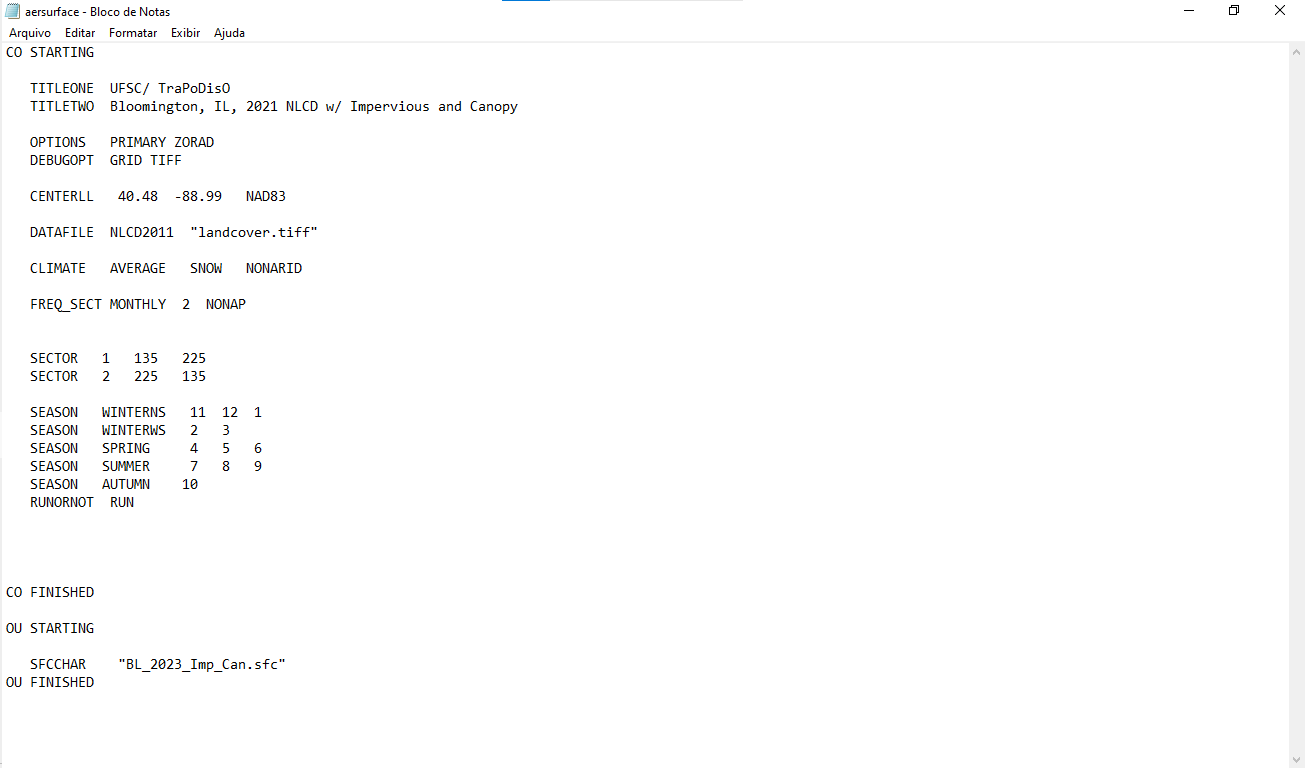
Create a new text file named `AERSURFACE.txt`. See Figure 13.
Figure 13
Below is an explanation of each command in the file:
- `CO STARTING` – Begins the control block.
- `TITLEONE`, `TITLETWO` – Custom titles for identification in output files.
- `OPTIONS PRIMARY ZORAD` – Requests default outputs and directionally-resolved Zo.
- `DEBUGOPT GRID TIFF` – Enables extra debug output (grid and TIFF info).
- `CENTERLL 40.48 -88.99 NAD83` – Geographic center of analysis.
- `DATAFILE NLCD2011 landcover.tiff` – Defines land cover classification and file.
- `CLIMATE AVERAGE SNOW NONARID` – Local climate parameters.
- `FREQ_SECT MONTHLY 2 NONAP` – Monthly values, 2 directional wind sectors.
- `SECTOR 1 135.00 225.00` – Sector 1 definition (SE–SW).
- `SECTOR 2 225.00 135.00` – Sector 2 definition (SW–N–SE).
- `SEASON WINTERNS 1 11 12` – Late Autumn/Winter season.
- `SEASON WINTER 2 3` – Winter with snow.
- `SEASON SPRING 4 5 6` – Transitional Spring.
- `SEASON SUMMER 7 8 9` – Midsummer.
- `SEASON AUTUMN 10` – Autumn with unharvested crops.
- `RUNORNOT RUN` – Executes the processing.
- `CO FINISHED` – Ends the control block.
- `OU STARTING` – Output file section.
- `SFCCHAR BL_2023_Imp_Can.sfc` – Output file name.
- `OU FINISHED` – Ends the output section.
2.5 Running AERSURFACE
Open the Command Prompt and navigate to the folder: `cd C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\1.AERSURFACE` See Figure 14.
Figure 14
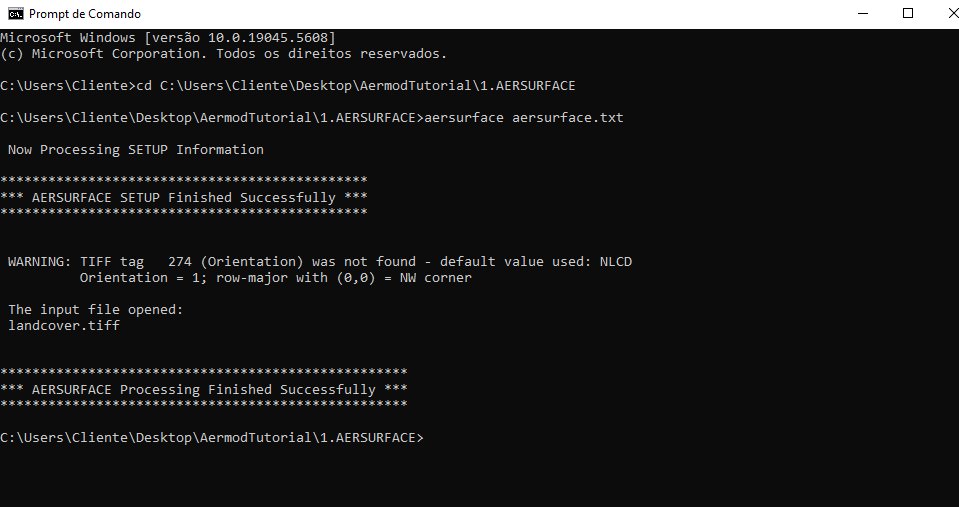
Then type the following to execute AERSURFACE: `aersurface aersurface.txt`
If successful, it should display output like in Figure 15.
Figure 15
5. AERSURFACE Output
Once complete, the `.sfc` file will be created — this contains the surface data. See Figure 16.
Figure 16
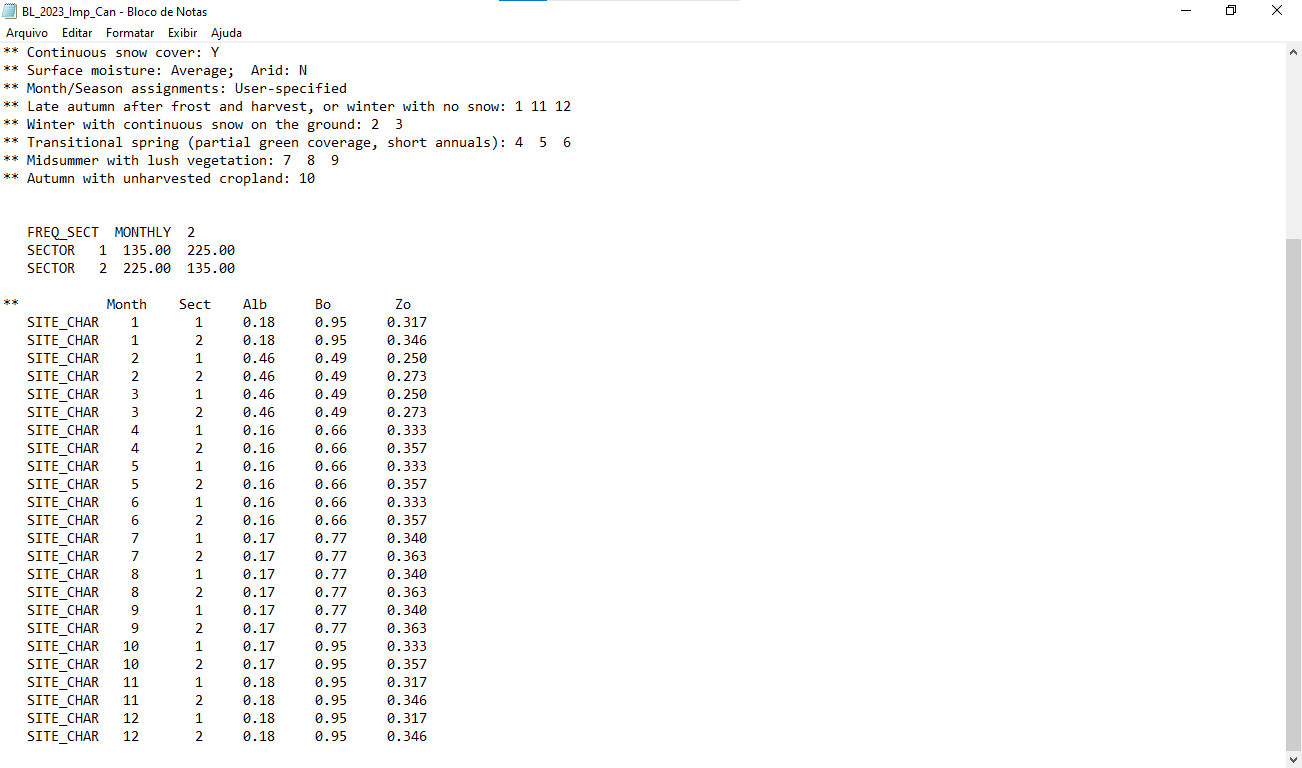
The following lines are an example of a surface characteristics file used by AERMET. Each line provides monthly values of albedo, Bowen ratio, and surface roughness length for a specific wind direction sector.
Example:
** Month Sect Alb Bo Zo SITE_CHAR 1 1 0.18 0.95 0.317 SITE_CHAR 1 2 0.18 0.95 0.346 SITE_CHAR 2 1 0.46 0.49 0.250 SITE_CHAR 2 2 0.46 0.49 0.273 SITE_CHAR 3 1 0.46 0.49 0.250
Column Descriptions
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| SITE_CHAR | Keyword indicating the start of a surface characteristics entry. |
| Month | Month of the year (1 = January, 2 = February, etc.). |
| Sect | Wind direction sector number. Defined in AERMET configuration. |
| Alb | Albedo — fraction of solar radiation reflected by the surface. |
| Bo | Bowen Ratio — ratio of sensible heat flux to latent heat flux. Reflects surface moisture conditions. |
| Zo | Roughness Length (in meters) — describes the aerodynamic roughness of the surface, affecting wind profile near the ground. |
Example Interpretation
For the line:
SITE_CHAR 1 1 0.18 0.95 0.317
This means:
- Month: January
- Sector: 1 (e.g., wind directions between 135° and 225°, if there are two sectors)
- Albedo: 0.18
- Bowen Ratio: 0.95
- Roughness Length (Zo): 0.317 meters
These values are used by AERMET to compute atmospheric stability and turbulence based on the physical characteristics of the surface surrounding the meteorological station.
Save this file to the folder ``C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\3.AERMET``: It will be used in AERMET's Stage 2 as a surface input.
Next Step
After finishing this step, you can continue to: AERMINUTE