This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
4. AERMAP
4.1 Introduction
AERMAP is a topographic preprocessor developed by the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) to support the atmospheric dispersion model AERMOD. It processes terrain elevation data, generating essential information about the relief that influences pollutant dispersion.
Primary Objective:
- Process topographic data to characterize the terrain in the study area.
- Generate elevation parameters used by AERMOD, such as terrain heights at each receptor/source, slopes, and obstacle effects.
Input Data
| Type | Description | Formats/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | Terrain altitude data | DEM files (USGS), SRTM, or ASTER |
| Source and Receptor Coordinates | Locations of emissions and analysis points | .DAT or .TXT files |
| Control Parameters | Processing settings (resolution, domain) | .INP or .TXT input file |
Outputs Generated
| File | Content | Use in AERMOD |
|---|---|---|
| .OUT (Main) | Terrain heights for sources and receptors | Defines topographic influence on dispersion |
| .HIL (Optional) | Elevation file in binary format | Visualization in GIS software |
| Reports (.RPT) | Processing logs and errors | Consistency verification |
Why is AERMAP important?
- Accuracy: Ensures AERMOD correctly accounts for terrain impact on pollutants.
- Efficiency: Automates complex elevation calculations for multiple points.
- Compatibility: Uses global topographic data standards (e.g., USGS).
See Figure 1:
Figure 1
4.2. Required Files for AERMAP
4.2.1. National Elevation Dataset (NED)
First, download the AERMAP executable from EPA AERMAP and extract the file to the folder C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP.
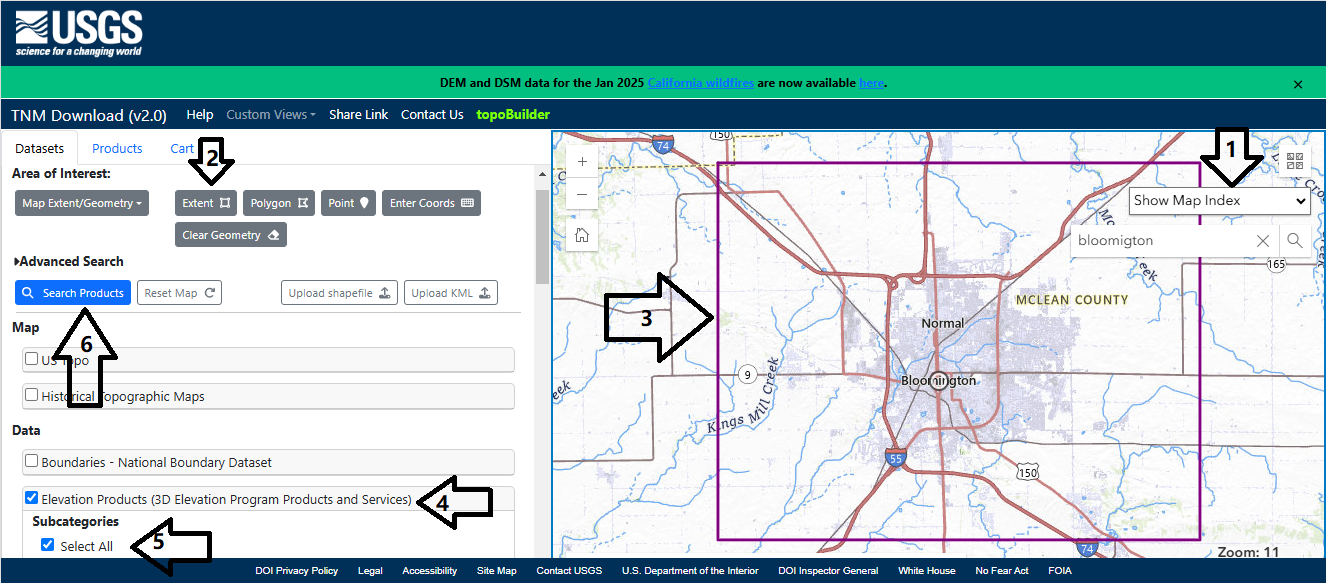
Next, visit: National Map to acquire elevation data for AERMAP. Follow the steps below, as shown in Figure 1:
Click the search bar and type Bloomigton, then select Bloomington, Illinois;
Adjust the zoom as shown in the figure and click Extent;
Select the region of interest by left-clicking to draw the area;
Check Elevation Products (3D Elevation Program Products and Services) under Data;
Check Select All under Subcategories;
Click “Search Products”.
Figure 1
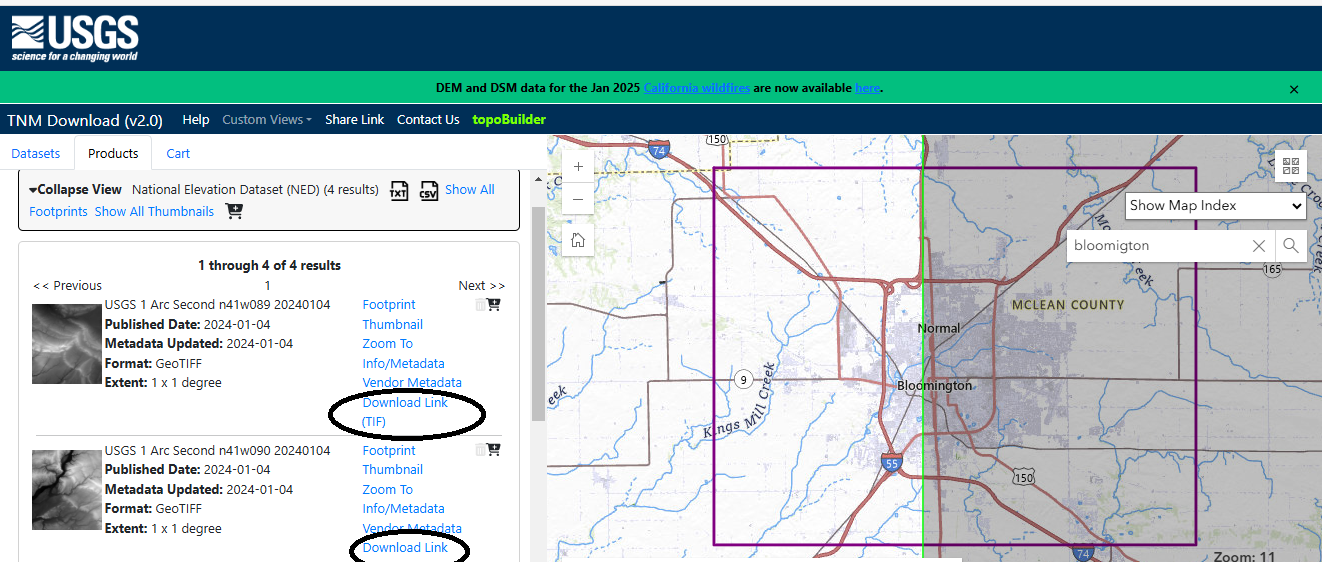
Now locate the data USGS 1 Arc Second n41w089 20240104 and USGS 1 Arc Second n41w090 20240104 and click their respective Download links, as shown in Figure 2:
Figure 2
Save the files to C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP and rename them to n41w089 and n41w090.
Create a subfolder named Seamless_dem within AERMAP and move the files n41w089 and n41w090 there.
Next, download a .Tif image converter to make these files compatible with the subprocessor (native .tif files are compressed).
Click conversao and extract it to the AERMAP folder. Open CMD and enter:
gdal_translate -of GTiff -co COMPRESS=NONE “C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP\Seamless_dem\n41w089.tif” “C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP\Seamless_dem\a1.tif”
Press Enter. Repeat for the other image:
gdal_translate -of GTiff -co COMPRESS=NONE “C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP\Seamless_dem\n41w090.tif” “C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP\Seamless_dem\a2.tif”
4.2.2. Receptors
A discrete receptor grid is available here. Extract it to C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP.
4.3. Configuring AERMET
With all inputs ready, configure AERMET. Create a text file named aermap with the following content:
CO STARTING TITLEONE UFSC/ TraPoDisO TITLETWO Bloomington, IL, 2024 NED Data File DATATYPE NED FILLGAPS DATAFILE .\Seamless_dem\a1.tif DATAFILE .\Seamless_dem\a2.tif DOMAINXY 300000 4470000 16 355784 4499506 16 ANCHORXY 333420 4482400 333420 4482400 16 4 RUNORNOT RUN CO FINISHED SO STARTING LOCATION STACK1 POINT 333415 4482405 SO FINISHED RE STARTING INCLUDED receptores_bloomington.dat RE FINISHED OU STARTING RECEPTOR Bloomington.rec SOURCLOC Bloomington.src OU FINISHED
Below is a description of each line:
Section CO – Control Options
| Line | Description |
| TITLEONE UFSC/ TraPoDisO | Project main title |
| TITLETWO Bloomington, IL, 2024 NED Data File | Additional description with location and data type |
| DATATYPE NED FILLGAPS | Specifies NED (National Elevation Dataset) data with gap interpolation |
| DATAFILE .\Seamless_dem\a1.tif | First GeoTIFF file containing elevation data |
| DATAFILE .\Seamless_dem\a2.tif | Second GeoTIFF file containing elevation data |
| DOMAINXY 300000 4470000 16 355784 4499506 16 | Defines lower-left and upper-right domain corners (UTM, zone 16N) |
| ANCHORXY 333420 4482400 333420 4482400 16 4 | Anchor point for internal grid alignment |
| RUNORNOT RUN | Command to start processing |
Section SO – Sources
| Line | Description |
| LOCATION STACK1 POINT 333415 4482405 | Defines a point source named STACK1 at the specified UTM coordinates |
Section RE – Receptors
| Line | Description |
| INCLUDED receptores_bloomington.dat | Imports the receptor list and coordinates file |
Section OU – Output
| Line | Description |
| RECEPTOR Bloomington.rec | Output file with receptor elevations/hill heights |
| SOURCLOC Bloomington.src | Output file with source elevations/hill heights |
4.4. Running AERMET
With aermap.txt ready, open CMD and navigate to C:\Users\Cliente\Desktop\AermodTutorial\4.AERMAP.
Type aermap aermap.txt and press Enter to generate AERMAP outputs. This may take time due to the high number of receptors per project.
Wait for the process to complete, and in the end, we will have the last two files required for the final execution of AERMOD:
- Bloomington.rec
- Bloomington.src
What is next?
Now we are almost finished; the only step left is to integrate all the data previously generated by AERMET and AERMAP in order to run them in AERMOD and obtain the output data we need
Attachment
Here you can download the folder I used to create this document. It is important that you use it only for comparison purposes or in case you are unable to make progress on the project. Attached: download.rar